QUESTION 248
Samuel a security administrator, is assessing the configuration of a web server. He noticed that the server permits SSlv2 connections, and the same private key certificate is used on a different server that allows SSLv2 connections. This vulnerability makes the web server vulnerable to attacks as the SSLv2 server can leak key information.
Which of the following attacks can be performed by exploiting the above vulnerability?
DROWN is a serious vulnerability that affects HTTPS and other services that deem SSL and TLS, some of the essential cryptographic protocols for net security. These protocols allow everyone on the net to browse the net, use email, look on-line, and send instant messages while not third-parties being able to browse the communication.
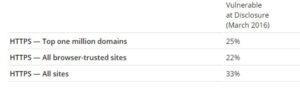
DROWN allows attackers to break the encryption and read or steal sensitive communications, as well as passwords, credit card numbers, trade secrets, or financial data. At the time of public disclosure on March 2016, our measurements indicated thirty third of all HTTPS servers were vulnerable to the attack. fortuitously, the vulnerability is much less prevalent currently. As of 2019, SSL Labs estimates that one.2% of HTTPS servers are vulnerable.
What will the attackers gain?
Any communication between users and the server. This typically includes, however isn’t limited to, usernames and passwords, credit card numbers, emails, instant messages, and sensitive documents. under some common scenarios, an attacker can also impersonate a secure web site and intercept or change the content the user sees.
Who is vulnerable?
Websites, mail servers, and other TLS-dependent services are in danger for the DROWN attack. At the time of public disclosure, many popular sites were affected. we used Internet-wide scanning to live how many sites are vulnerable:
Operators of vulnerable servers got to take action. there’s nothing practical that browsers or end-users will do on their own to protect against this attack.
Is my site vulnerable?
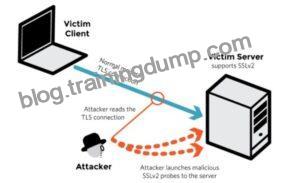
Modern servers and shoppers use the TLS encryption protocol. However, because of misconfigurations, several servers also still support SSLv2, a 1990s-era precursor to TLS. This support did not matter in practice, since no up-to-date clients really use SSLv2. Therefore, despite the fact that SSLv2 is thought to be badly insecure, until now, simply supporting SSLv2 wasn’t thought of a security problem, is a clients never used it.
DROWN shows that merely supporting SSLv2 may be a threat to fashionable servers and clients. It modern associate degree attacker to modern fashionable TLS connections between up-to-date clients and servers by sending probes to a server that supports SSLv2 and uses the same private key.
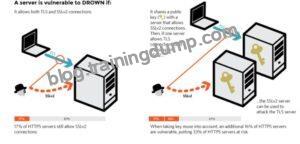
A server is vulnerable to DROWN if:
It allows SSLv2 connections. This is surprisingly common, due to misconfiguration and inappropriate default settings.
Its private key is used on any other serverthat allows SSLv2 connections, even for another protocol. Many companies reuse the same certificate and key on their web and email servers, for instance. In this case, if the email server supports SSLv2 and the web server does not, an attacker can take advantage of the email server to break TLS connections to the web server.
How do I protect my server?
To protect against DROWN, server operators need to ensure that their private keys software used anyplace with server computer code that enables SSLv2 connections. This includes net servers, SMTP servers, IMAP and POP servers, and the other software that supports SSL/TLS.
Disabling SSLv2 is difficult and depends on the particular server software. we offer instructions here for many common products:
OpenSSL: OpenSSL may be a science library employed in several server merchandise. For users of OpenSSL, the simplest and recommended solution is to upgrade to a recent OpenSSL version. OpenSSL 1.0.2 users ought to upgrade to 1.0.2g. OpenSSL 1.0.1 users ought to upgrade to one.0.1s. Users of older OpenSSL versions ought to upgrade to either one in every of these versions. (Updated March thirteenth, 16:00 UTC) Microsoft IIS (Windows Server): Support for SSLv2 on the server aspect is enabled by default only on the OS versions that correspond to IIS 7.0 and IIS seven.5, particularly Windows scene, Windows Server 2008, Windows seven and Windows Server 2008R2. This support is disabled within the appropriate SSLv2 subkey for ‘Server’, as outlined in KB245030. albeit users haven’t taken the steps to disable SSLv2, the export-grade and 56-bit ciphers that build DROWN possible don’t seem to be supported by default.
Network Security Services (NSS): NSS may be a common science library designed into several server merchandise. NSS versions three.13 (released back in 2012) and higher than ought to have SSLv2 disabled by default. (A little variety of users might have enabled SSLv2 manually and can got to take steps to disable it.) Users of older versions ought to upgrade to a more moderen version. we tend to still advocate checking whether or not your non-public secret is exposed elsewhere Other affected software and in operation systems:
Instructions and data for: Apache, Postfix, Nginx, Debian, Red Hat
Browsers and other consumers: practical nothing practical that net browsers or different client computer code will do to stop DROWN. only server operators ar ready to take action to guard against the attack.

